Solving Cybergym CTF Lab1.
This writeup describes the process carried out to solve the Cybergym Android CTF Lab1 with some mitigation techniques. The aim of this CTF is to retrieve the passcode needed to view the flag on the application.
Cybergym has developed some cool applications for android CTF which you can access from here.
So lets start digging into the application.
First we need to download the application and install it into our genymotion emulator device. You can either build the application by cloning into the repository or can directly download the APK file from here.
Lets download it from the terminal.
Install the application on genymotion emulator using ADB.
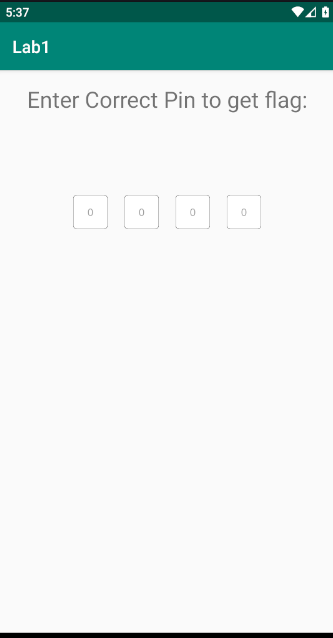
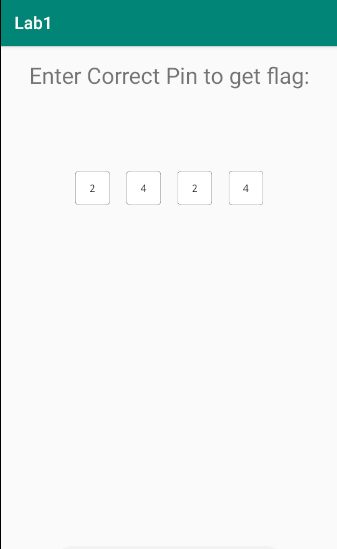
The application looks like this where we need to enter the correct PIN in order to get the flag.
Lets decompile the application using Apktool and Jadx. Here both the tools are used to decompile the application but both have their own purposes. Apktool is used in-case the application needs to be recompiled again and Jadx is used to view the source code in Java.
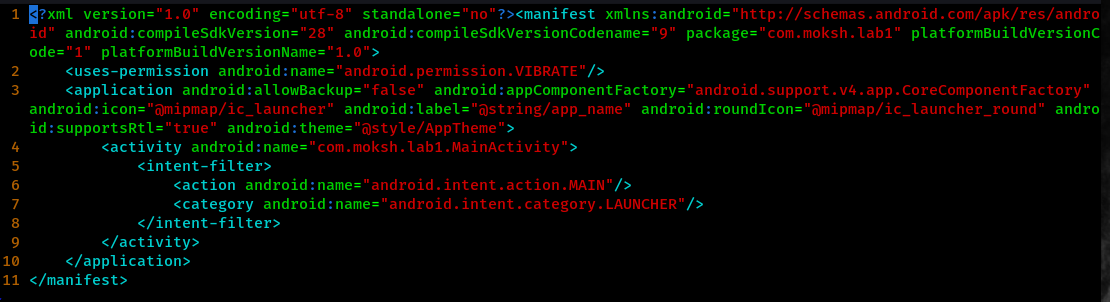
The first approach after decompiling the application is to analyze the AndroidManifest.xml file which provides us the brief overview of the application. It is also analyzed to identify if unnecessary activities, services, providers and receivers are exported or not. Similarly deeplink link issues and much more. For now lets stuck to the manifest file.
Here we do not found any issues on the manifest file.
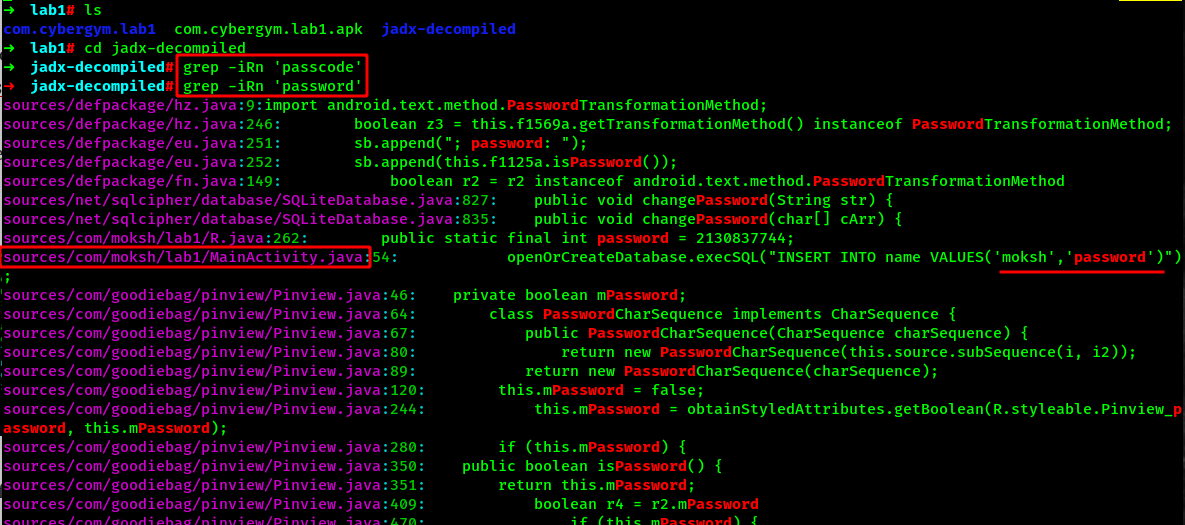
Since the CTF is about find the passcode. Lets dig into the source code and view if the keyword like passcode or password is available. Navigate into the directory created by Jadx to view it on Java syntax.
As we can see here some suspicious credentials have been hardcoded into the file MainActivity.java. Lets open the file.
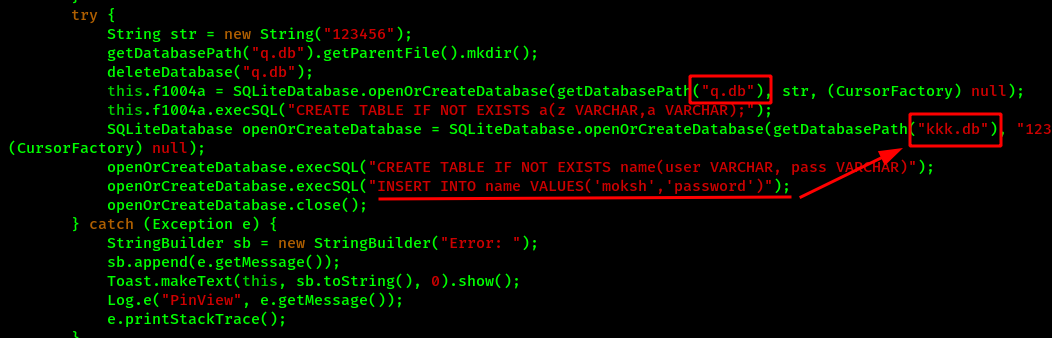
Here we found that there are two databases which can have the PIN number that we needed to get the flag. However I might be wrong too. But lets assume and focus on this approach.
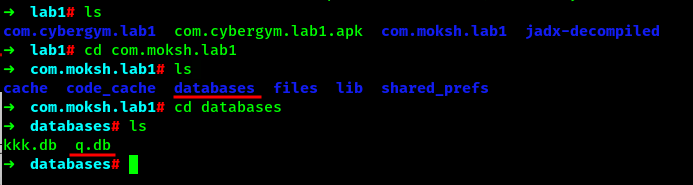
Also lets narrow down it more. We know that we need 4 digits PIN number for solving this CTF but the database kkk.db is storing the values usernames and password which have more characters. So for now, we can more focus on the database q.db.
Lets analyze how the database is built and what values are stored on the database.
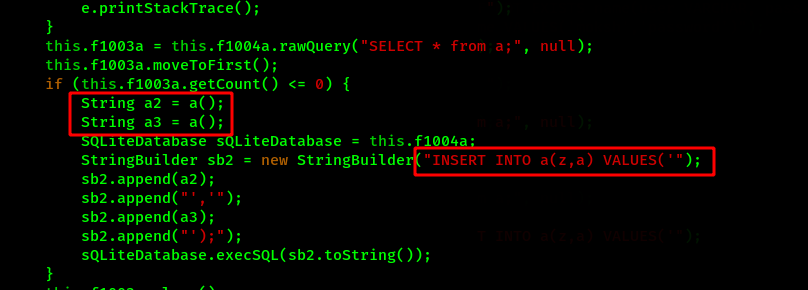
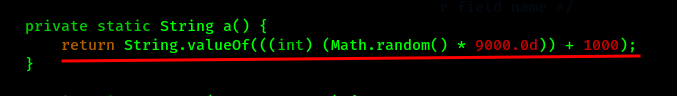
Here we can see the database consists of two columns named as z and a. Also a function a() is called everytime while the values needs to be inserted into the column.
We can also find the function a() in the same MainActivity.java file which returns some random numerical values. This means the PIN which we require is different in every device and is changed everytime the application is opened.
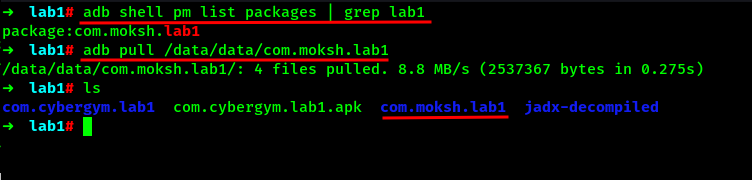
For now, lets pull the internal storage of the application which is located on the /data/data directory of the android phone followed by the package name. We will find the package name at first and pull the internal storage of the package with ADB.
Lets navigate into the directory and find out q.db file.
Now we can simply run sqlite command to view the values into the database. But…
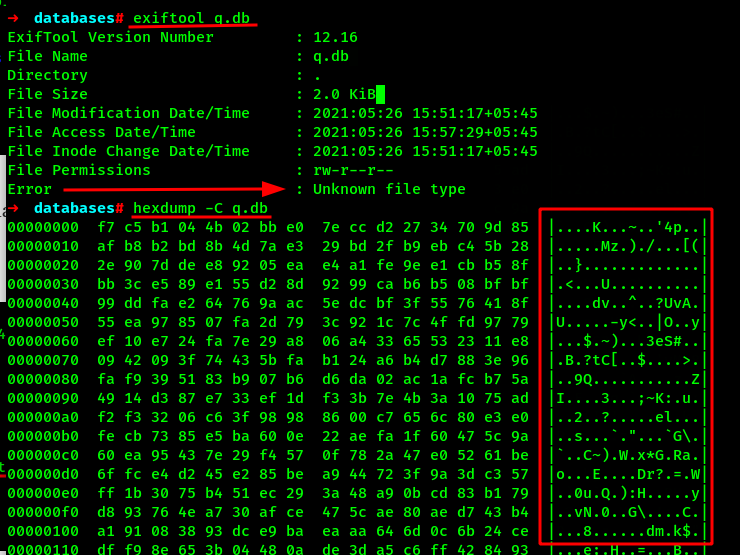
But the database files is not a database file??? What if the database file is encrypted or corrupted?? Lets check it with exiftool and hexdump.
We can see the file type is not recognized by the exiftool and the database values in the hexdump is a JUNK. Lets search on the google if the android database file can be encrypted. !!! Research !!!
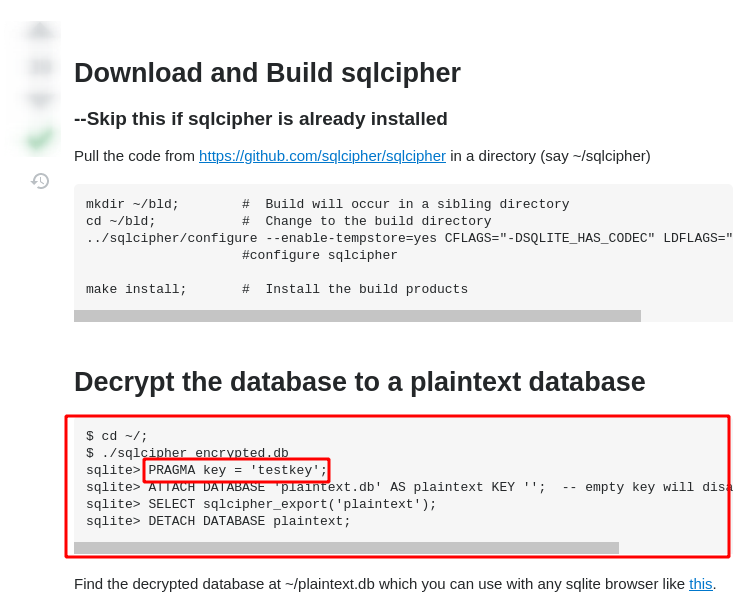
Here we found that SQLCipher can be used to encrypt the database files in android. Lets search for the method to decrypt the database with SQLCipher.
Here we can decrypt the database using SQLCipher but we need a key for it. Lets find the key if it lies on the source code as well i.e. MainActivity.java.
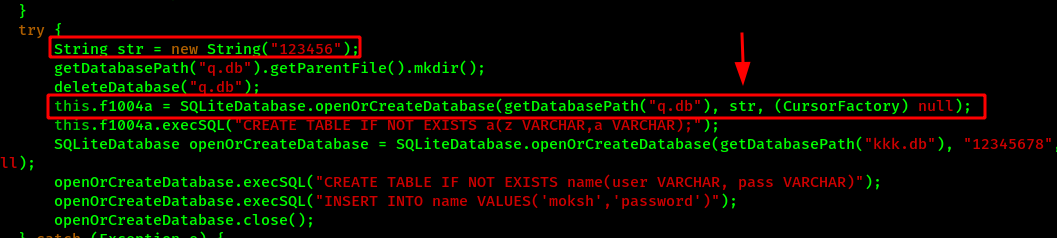
Here we can see that a str variable is passed on the database creation method. And the str variable have the value 123456 which might be the key. The database is encrypted using SQLCipher by passing the secret key during the database creation time. Also every time the database needs to be accessed, the key is needed, which is done with openOrCreateDatabase() method.
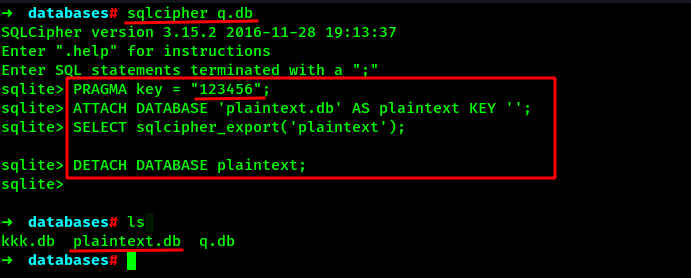
Lets use 123456 as the Pragma key and decrypt the database.
Here what we have done is used 123456 as the key to decrypt the database, created a new database called plaintext.db and inserted all the values from q.db to it. Also no any key is passed on the plaintext.db database so that it wont get encrypted. After that, can have a new database in the directory as shown above.
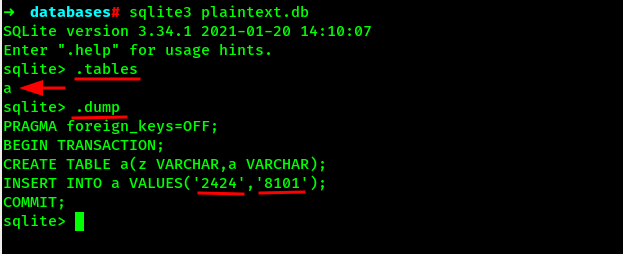
Lets dump the new unencrypted database using sqlite3.
Here we can see the two random numbers on a table which can be the PIN we have been hunger of from the beginning.
Lets enter the PIN on the application and see if we can get the flag.
Yes!!! You did it Morty…….
In conclusion, there are plenty of vulnerabilities chained in this challenged. The sensitive information like credentials, PIN numbers are stored on the local database which should be avoided. However the database is encrypted using SQLCipher but the key is hardcoded. The secret key should not be hardcoded on the source code. It can be stored on the server side or on the android keystore.
#AndroidPentesting
#AndroidCTF